Background
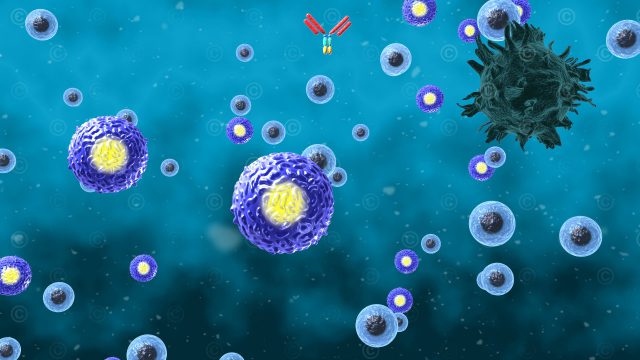
Psoriatic arthritis (psoriatic arthritis or psoriatic arthritis) is a chronic inflammatory joint disease. It is an autoimmune disease, i.e. the cells of the immune system attack the body’s own healthy cells. Psoriatic arthritis occurs in around one in three people who suffer from psoriasis. The malfunctioning activity of the immune system causes inflammation in the joints, which leads to pain, stiffness and swelling. The disease often affects the joints of the fingers and toes, but can also affect larger joints such as the knees, hips or spine.
Project description
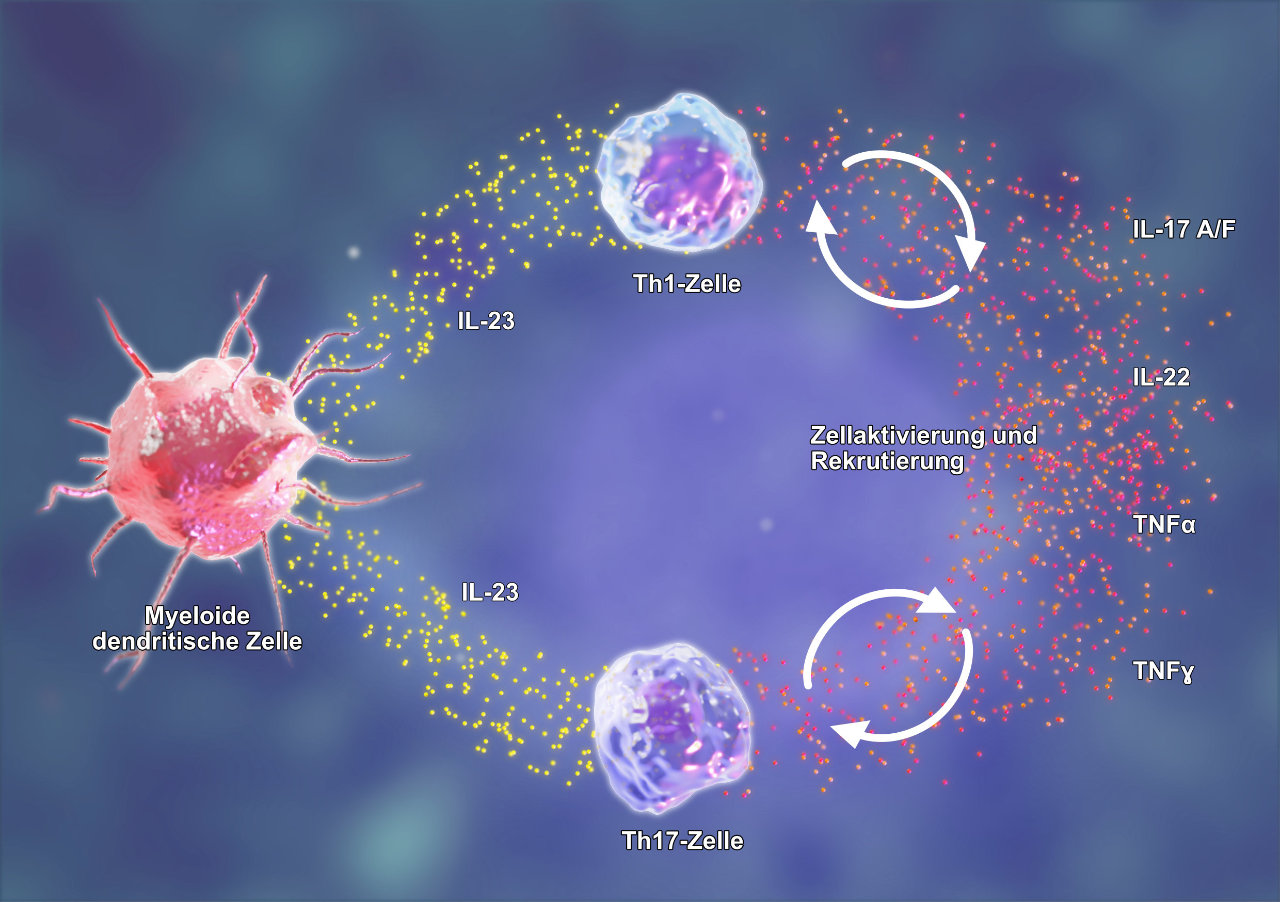
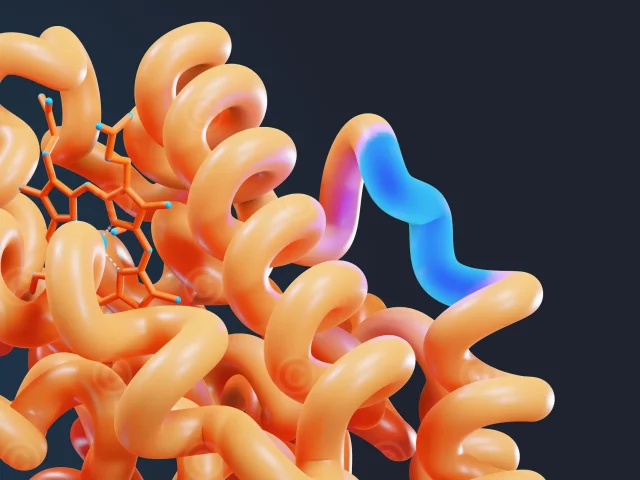
Design of an illustration of the mode of action of Tremfya/Guselkumab in psoriatic arthritis. Guselkumab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the activity of interleukin-23 produced by myeloid dendritic cells. Guselkumab thereby reduces the differentiation and activation of Th17 cells and the consequent recruitment of pro-inflammatory substances such as IL-17/AF, IL-22, TNF-α, and TNF-γ. In addition, it influences the differentiation and activation of monocyte-like cells and acts on TRM memory cells (tissue-resident memory cells) in the skin. These effects reduce the inflammation of the skin and joints and slow down the progression of the disease.
Project details:
Content: 2 illustration
Utilization: Publications online and print
Specifications: DIN A3 (~4000*3000px)
Client: swot / Janssen
The rights of use of the images shown here belong to the client, use is not permitted. The images are protected with watermarks
Illustrations