Usage rights : client -nda-
Music: Kevin McLeod – As I figure – License: Creative Commons (CC BY 3.0)
Oral and transdermal administration are two common methods of delivering active ingredients to the body.
In oral administration, the active ingredient is taken orally, i.e. usually in the form of a pill or capsule, and then absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract. In transdermal administration, the active ingredient is applied to the skin and then absorbed through the skin.
With oral administration, bioavailability may be lower than with transdermal administration because the active ingredient may be metabolized in the liver and digestive tract, reducing the amount of active ingredient that enters the bloodstream. Transdermal administration, on the other hand, may have higher bioavailability because the active ingredient is absorbed directly into the bloodstream without being metabolized in the liver or digestive tract.
Oral administration may have a slower onset of action because the active ingredient must first be absorbed through the digestive tract before it enters the bloodstream. However, the duration of action may be longer because the active ingredient may be released slowly over time. Transdermal administration may have a faster onset of action because the active ingredient is absorbed directly into the bloodstream, but the duration of action may be shorter because the active ingredient is rapidly metabolized and excreted from the body.
Design a comparative animation on the benefits of transdermal administration of an active ingredient compared to oral ingestion. Summary animation on the key features of the active ingredient.
Project details:
Content: 5 animations, ~1:25 min.
Utilization: e-detailling iPad of sales representative
Specifications: Resolution 2732*2048px (iPad Pro)
Client: -nda-
The rights of use of the illustrations shown are with the respective clients.
Screenshots animation:
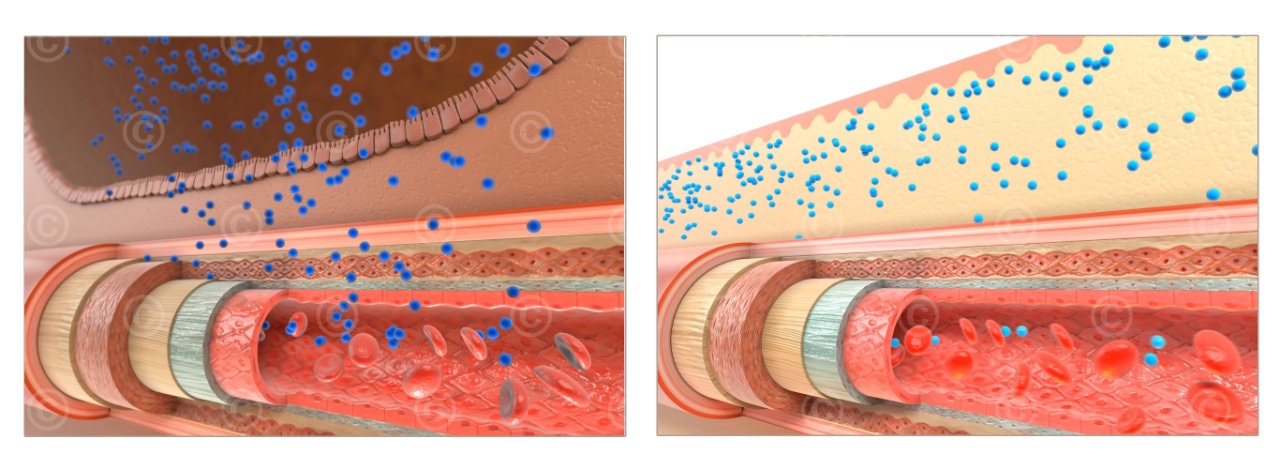
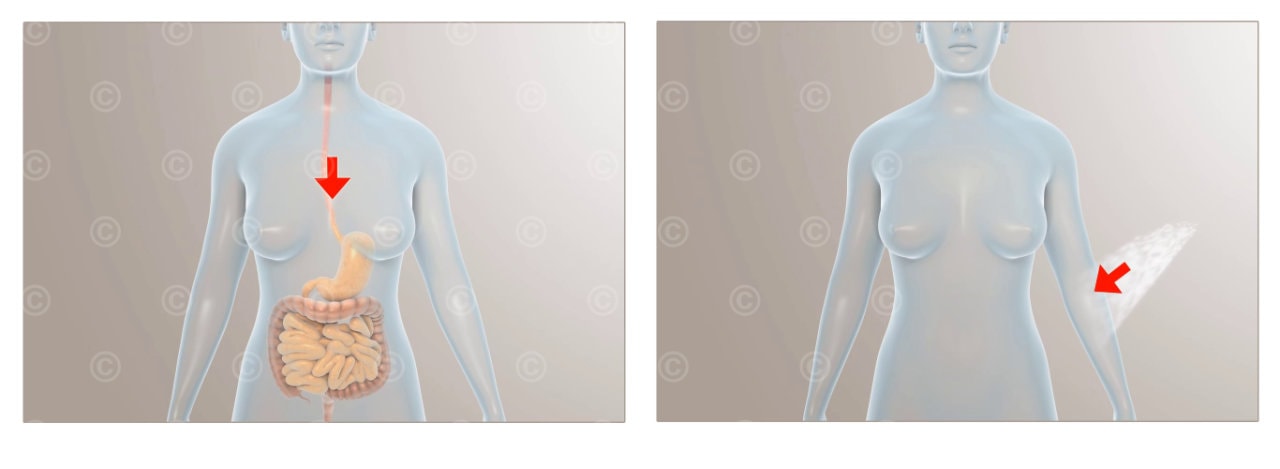
Comparison of oral (left) and transdermal (right) administration of an active substance
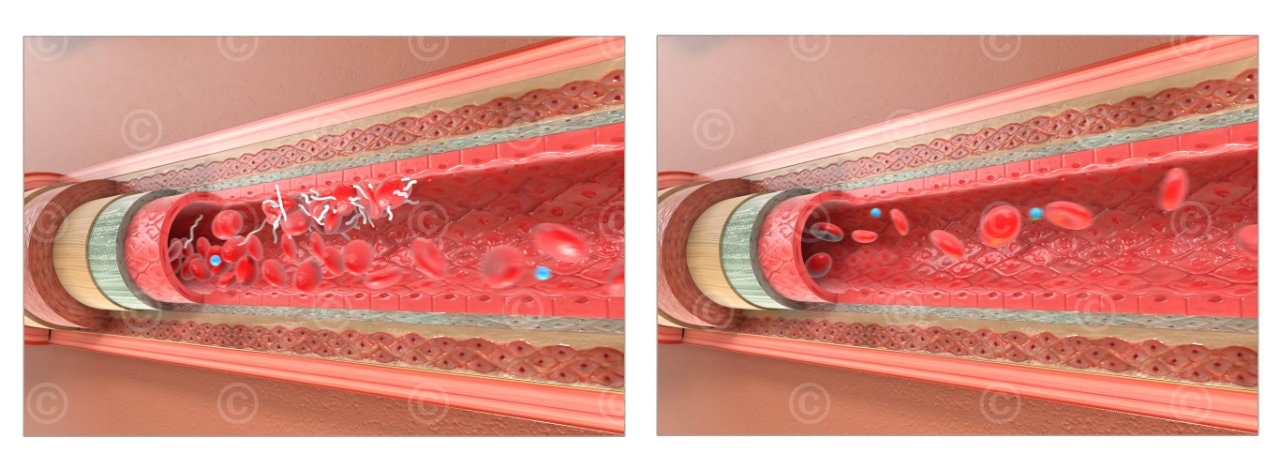
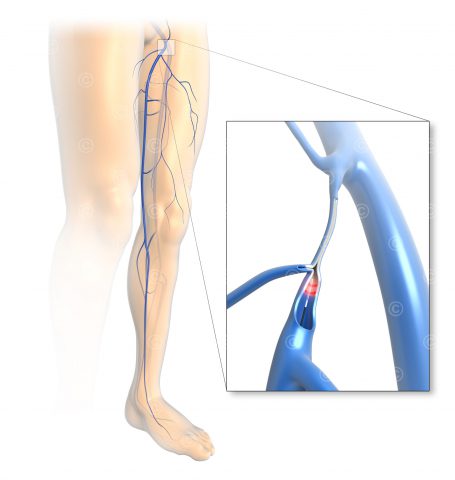
Possible thrombo-embolic events with oral drug (left)